A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. A capacitor consists of two conductors separated by a non-conductive region. The non-conductive region is called the dielectric. In simpler terms, the dielectric is just an electrical insulator. Examples of dielectric media are glass, air, paper, vacuum, and even a semiconductor depletion region chemically identical to the conductors.
Capacitance of a capacitor can be defined as the ratio of the charge on two plates to the applied voltage.
For capacitors in parallel

For capacitors in series
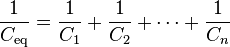
The reactance and impedance of a capacitor are respectively
Capacitance of a capacitor can be defined as the ratio of the charge on two plates to the applied voltage.
C=Q/V
Where Q = Charge on both plates
V = Applied voltage
Another equation for capacitance is
Where d = distance between two plates
A = Area of the plates
Capacitors in a parallel configuration each have the same applied voltage. Their capacitances add up. Charge is apportioned among them by size. Using the schematic diagram to visualize parallel plates, it is apparent that each capacitor contributes to the total surface area.

For capacitors in series
Connected in series, the schematic diagram reveals that the separation distance, not the plate area, adds up. The capacitors each store instantaneous charge build-up equal to that of every other capacitor in the series. The total voltage difference from end to end is apportioned to each capacitor according to the inverse of its capacitance. The entire series acts as a capacitor smaller than any of its components.
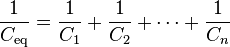
.jpg)


